If you just can’t stop checking Instagram, why not make a profession out of it?
Data analysts explore trends across a wide variety of fields.
Working in industries like tech, finance, and health care, they figure out the answers to important questions.
Data analysts perform or gather research on the way products, services, and relationships impact consumers.
This allows them to influence how companies do business.
The data analyst’s databases are filled with information gleaned from social media, sales and marketing reports, and consumer feedback.
They transform piles of information into the key to unlock more efficient and successful methods for communicating, creating, and marketing.
Data Analyst Information
| Official Job Title | Data Analyst |
| Average Salary | $70,417 |
| Stress Level | High |
| Work/ Life | High |
| Job Satisfaction | Low |
| Career Advancement | Average |
Data Analyst Job Description
What Is A Data Analyst?
A data analyst is someone who gathers information and performs research for the betterment of the company they work for.
Data analysts work in a number of different industries, including the financial sector, healthcare, technology, and government.
You will find data analysts on the job in social media and tech companies, as well as most banking and financial companies.
In addition, data analysts work for government entities such as the Department of Labor.
What Does A Data Analyst Do On A Daily Basis?
Data analysts compile and examine data relevant to their respective industries.
Depending on the field, data analysts may conduct research themselves or analyze the research of others to spot trends, determine outcomes, or better prepare the company to meet consumer expectations.
Business and financial analysts explore market fluctuations and investment data, while data analysts at tech companies may calculate the user response to new features or discover correlations between user profiles and online behavior.
Understanding how and why consumers make purchases, use products, and respond to marketing campaigns is all part of a day’s work for many data analysts.
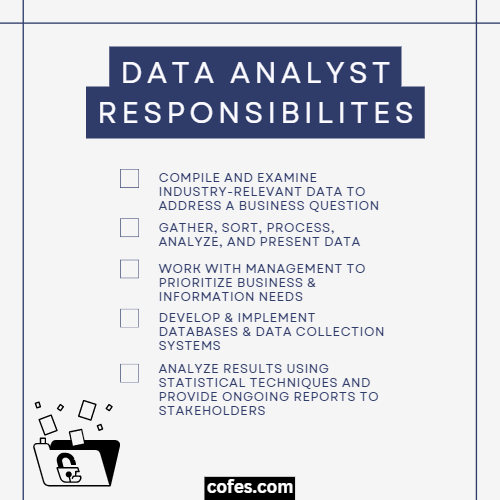
Responsibilities, Duties & Roles Of A Data Analyst
The job of a data analyst is to study results and determine factors that affect a wide range of decisions.
Data analysts conduct research that helps the employer make informed choices about everything from product lines and marketing to daily operations and hiring.
Data analysts need to collect information from a variety of sources.
They may examine sales reports or marketing campaigns to study the effectiveness of different options, perform testing to determine the wisest choice, or conduct customer surveys and feedback queries.
Data analysts are also responsible for sharing their findings with managers and department leaders.
Data Analyst Salary
Average Salary
The average annual salary for a data analyst in the United States is $70,417, according to Glassdoor.
On the low end, data analysts earn $56,000/year, while annual earnings can reach $108,000 for the more experienced professionals.
For newcomers into the field, the entry-level salary data analysts can expect is $47,791/year, according to ZipRecruiter.
Candidates with relevant experience or education will sometimes start higher.
Senior-level salary averages between $80,000-$150,000, according to Glassdoor.
Factors including company size, how many individuals report to the analyst, and educational background make a big difference in determining salary structure.
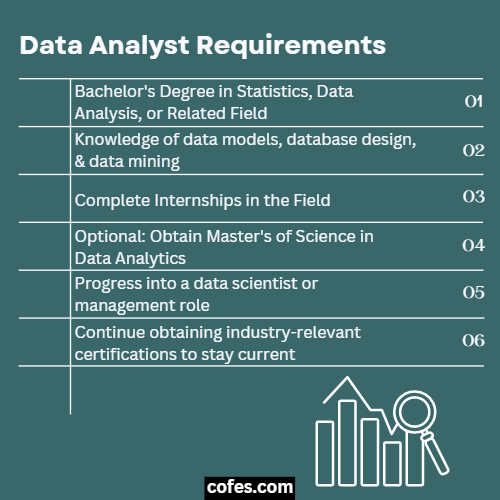
How To Become A Data Analyst
The Entry Level: Certification, Training & Degree
Becoming a data analyst almost always requires a 3–4-year university degree.
Interested candidates should study data science/data analysis, economics, statistics, computer sciences, or mathematics.
After completing post-secondary education, candidates will want to apply for entry-level positions as Junior Analysts or Data Analysts I.
A university degree is usually sufficient, but to stand out, some candidates seek formal certification through CompTIA, Microsoft, or IBM.
Other Skill Sets, Requirements & Qualifications
Data analysts must be computer literate and comfortable working with a variety of software and programming languages.
Understanding SQL, R, Python, or other database languages is essential for most positions.
Certification from a respected school, company, or organization is desirable.
There are many exams data analysts can sit in order to progress to higher stages of their careers and command a higher salary.
Data analysts also need to enjoy research and be capable of using numbers to determine trends.
The ability to make clear graphs and charts as well as write formal reports or white papers is considered a requirement for nearly all positions.
How Long Does It Take To Become A Data Analyst?
Candidates can apply for the position immediately after finishing university.
Expect to spend 3-4 years studying for a relevant degree and an additional 1-5 years working as a lower-level or junior analyst before becoming a fully-fledged data analyst.
Is It Hard To Become A Data Analyst?
Becoming a data analyst can be difficult as it requires precision, determination, and strong mathematical skills.
However, it is an entry-level position open to qualified applicants.
The work can be done as a freelancer or consultant early in the career.
For a candidate with the right background and determination, becoming a data analyst should not prove difficult.
Data Analyst Career Paths
The Data Analyst Roadmap
After completing a university degree, employees start as Data Analysts I or Junior Analysts.
Once the candidate has completed several years of work, it is possible to move up to Data Analyst II.
The career trajectory then works through Senior Analyst, Lead Data Scientist, and finally, Chief Technology Officer.
Many senior-level data analysts and above have master’s or doctorate degrees in data analysis or a related field.
Projections For Growth In Data Analyst Jobs
Data analysts are highly sought after in many industries, and projections for the future are strong.
The anticipated growth rate is 25% over the next ten years.
In Summary: Is Data Analyst A Good Career?
Being a data scientist is a good career for someone who is capable of close attention to detail and who enjoys research.
However, many data analysts report dissatisfaction with their jobs.
Some data analysts burn out because of the difficulty of their work and the demands placed on them by employers.
Still, others enjoy the career and find it highly rewarding.
Compensation is high, with incoming data analysts capable of earning salaries comparable with what senior-level employees in other fields can command.
Growth potential is also high.
Working Conditions
Can A Data Analyst Work Remotely From Home?
Much of the work of a data analyst can be performed remotely.
In fact, some data analysts work as freelancers from home and make their services exclusively available online.
Most of the everyday tasks of data analysis can be done on computers while traveling or working from home.
How Many Hours Does A Data Analyst Work?
In some companies, data analysts work a consistent 40-hour/week schedule and are on the job during office hours.
However, freelance data analysts and some employees may work unpredictable hours.
Hours can fluctuate depending on the industry in question.
During slow times, data analysts may work 30 hours/week or less, while busy seasons call for 50+ hours/week.
Some data analysts work outside office hours, particularly if they work remotely.
Can A Data Analyst Work Part-Time?
Part-time data analyst positions are available.
These are typical with small businesses or large companies which have a full data analysis team on staff.
Freelance data analysts may also be brought in on a per-project basis.
What Are The Average Vacation Days Of A Data Analyst?
Full-time data analysts receive generous vacation benefits packages with an average of 21 paid days of holiday leave as well as paid sick time and official holidays off.
Senior-level data analysts enjoy as many as 30 days of paid vacation annually.
Part-time data analysts rarely receive paid time off but may have as many as seven paid vacation days each year.
Freelance data analysts are not provided paid or unpaid leave.
Alternative Careers & Similar Jobs to a Data Analyst
- Budget Analyst
- Operations Analyst
- Sales Analyst
- Business Analyst
- Financial Analyst
- Market Research Analyst
- Business Development Manager
- Auditor
- Finance Manager
Data Analyst Resume Tips
Start the resume with a concise summary of your skills and experiences.
This allows hiring managers to immediately see whether you have the abilities they are looking for.
Then list your relevant work history in reverse-chronological order, with the newest work on top.
Leave off irrelevant work history to keep it one page in length.
Consider including links to significant projects if you’ll be submitting the resume digitally.
Don’t forget to list any degrees, certifications, courses, or organization memberships relevant to the job requirements.
Data Analyst Interview Questions
Q1: Describe how your education or work history has prepared you for this position.
Why it works: Finding out the applicant’s level of experience is useful for determining whether they are capable of managing the tasks required of them.
As some data analysts come without previous relevant work history, they should be able to explain how their past education helped get them ready for this job.
Look for specific projects, tools, or skills the applicant learned.
They may also be able to share how personal projects taught them some skills they will be using.
Q2: What tools do you expect to use for this position?
Why it works: Data analysis tools like Solver and RapidMiner are essential for most data analyst positions.
Qualified candidates will be familiar with a number of professional tools and resources, even if they haven’t had much experience with them yet.
This question also informs the hiring manager whether the candidate understands the job requirements and has researched the company.
Passionate applicants will have some background information about the business and should be able to anticipate how certain tools will help them in their duties.
Q3. Can I see your portfolio?
Why it works: Prepared candidates will have a portfolio or samples of their past work.
Even those starting as entry-level employees should have prepared some projects during their degree or independently.
Asking a candidate to go through a case study helps the hiring manager understand the thought process and gauge familiarity with certain tools and resources.
If the candidate doesn’t have a portfolio, the hiring manager could present them with a scenario and ask about the steps for working through the problem.
Q4. What is a normal distribution?
Why it works: Understanding probability and variability is essential even for entry-level data analysts.
Applicants should have learned about the bell curve or normal distribution in secondary school or at university.
Any qualified applicant should clearly understand concepts such as the mean, variables, and Gaussian curve.
If an interviewee cannot answer this type of question, they are likely unprepared for the job of Junior Analyst and will need more education or on-the-job training before tackling a data analyst position.
Jobs Related To Data Analyst
- Actuary
- Business Analyst
- Business Intelligence Analyst
- Business Intelligence Officer
- Chief Technology Officer
- Data Journalist
- Data Scientist
- Financial Analyst
- Forensic Accountant
- Machine Learning Engineer
- Market Researcher
- Marketing Analyst
- Operations Analyst
- Quality Engineer
- Quantitative Analyst
- Research Analyst
- Risk Analyst
For the HR Manager: Tips For Hiring A Data Analyst
Key Characteristics To Look For In A Data Analyst
- Analytical:
- A data analyst must be able to look at things from an analytical perspective.
- They should be interested in figuring out answers to complex problems.
- Getting to the root of why certain functions occur or particular choices are made is a vital part of the job.
- Being a data analyst requires using verified facts instead of emotions or intuition.
- Looking at a problem and determining logic-based solutions is important for being a successful data analyst.
- Creative:
- Although analysts deal in facts and figures, they must be creative enough to consider a variety of possibilities when figuring out a problem.
- Many problems are complex, and there may be numerous reasons behind them.
- Instead of being satisfied with the most obvious conclusion, data analysts should be able to engage in creative thinking to discover alternative issues and non-obvious solutions.
- Creative thinking allows the data analyst to try new ways of resolving complex problems and evaluating information.
- Mathematical:
- Much of the work of data analysts involves mathematics, economics, and statistics.
- Someone who considers themselves poor at math would struggle with data analysis because the job requires working with numbers to determine outcomes.
- Mathematical ability also helps data analysts learn programming languages and aid in machine learning.
- This is also a basis for building technical skills, which is important for analysts who perform testing or work in technology.
Minimum Level Of Education & Experience
Becoming a data analyst requires a minimum of a 3–4-year post-secondary degree.
The degree subject should be mathematics, statistics, data science, computers, or economics.
The junior-level position is considered entry-level and open to qualified candidates with a university degree.
Certification is optional but places candidates ahead of the competition.
No past experience is necessary, but independent or academic projects look good on resumes and portfolios.
